Trench Drain Systems:
Components & How to Choose the Right Drainage System
Trench Drain Systems:
Components & How to Choose the Right Drainage System
<h2><span class="text--big"><strong>What is a Drainage System?</strong></span></h2><p>Drainage is the process of removing excess water and moisture from an area. It is essential for maintaining the integrity of infrastructures and residential areas. Modern drainage systems feature collectors – such as trench drains – and pipe networks that convey stormwater runoff or other liquid waste to disposal points. They are critical components of many structures and environments. Without drainage systems, excess water infiltrates the foundation of buildings, leading to <strong>structural damage and financial costs. </strong></p><p> </p><p>Several factors determine the design of a drainage system: </p><ul><li>Rainfall frequency and intensity</li><li>Soil type</li><li>Configuration</li></ul><p> </p><p>Drainage systems also take various forms. You will find frame and grate systems, prefabricated trench drains with grates and slot drains. Each style is appropriate for specific water management needs.</p><p>A <strong>trench drain</strong> is a linear drain covered with a grate that removes excess surface water. Trench drainage systems are prevalent as they are inconspicuous and come in different styles and materials. Users can configure trench drains for streets, industrial sites, and domestic settings.</p>
<h2><span class="text--big"><strong>How Do Drainage Systems Work?</strong></span></h2><p>Drainage relies on gravity to divert excess water. Water will always flow downhill. Drainage systems use strategically designed gradients to channel water from one place to another.</p>
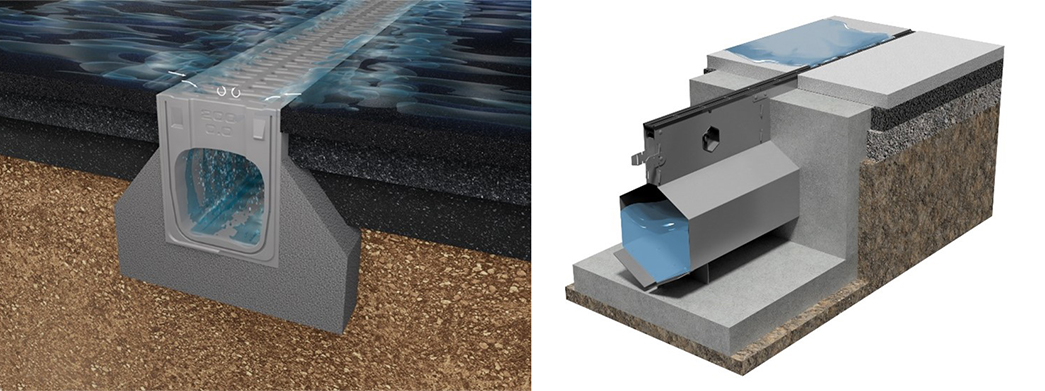
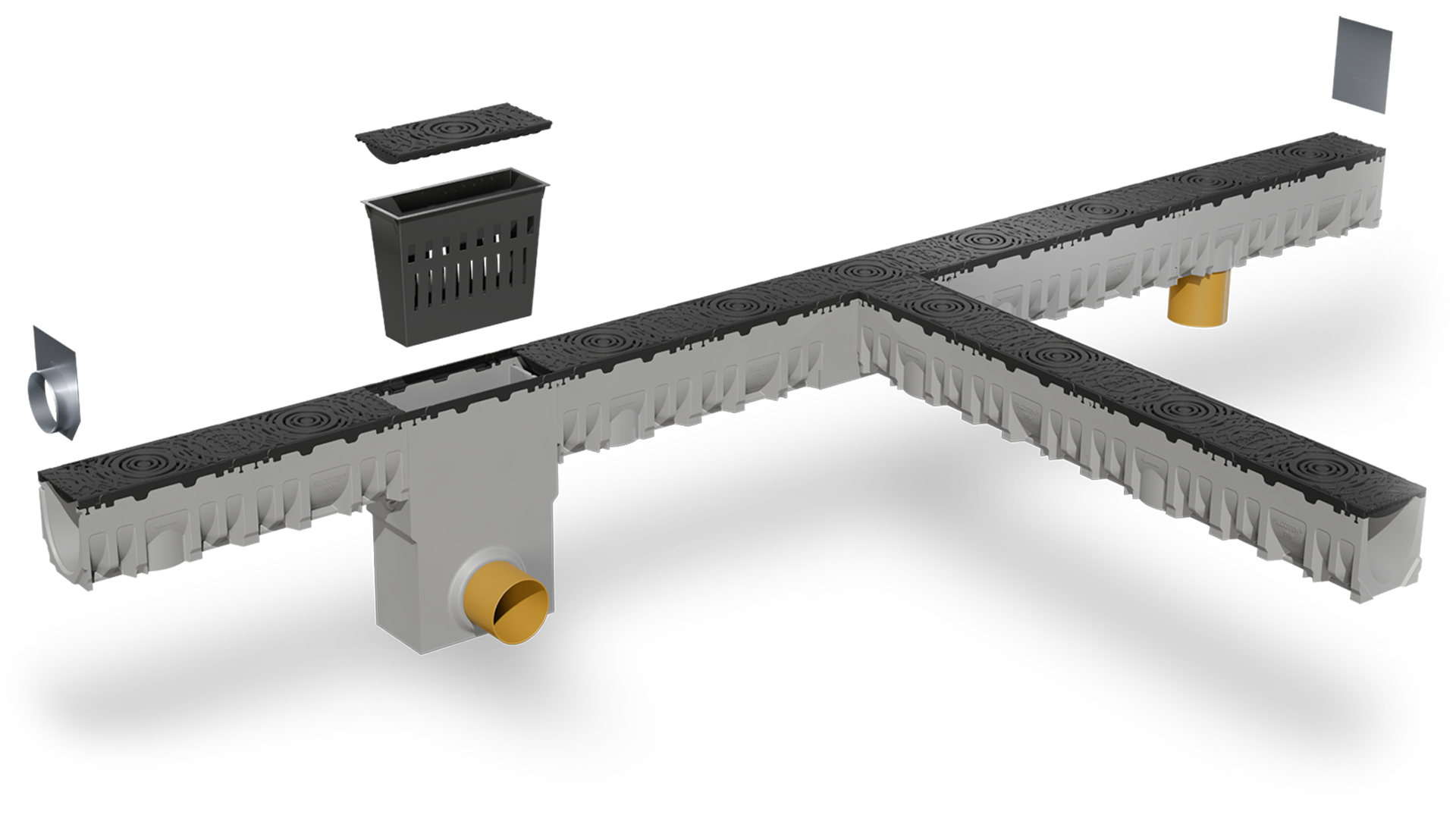
<p>Drainage occurs through a network of channels, grates, and pipes. After being gathered via several grates and channels, the water flows to an outflow or catch basin for additional processing or evacuation. The efficiency of this process depends on the correct selection and installation of each component within the system.</p><p>The drain pipe in your building connects to a city-wide network of pipelines. This complex piping system handles water from sites across the surrounding region - preventing flooding and removing waste. The importance of these functions means one minor hitch can cascade into a huge problem affecting an entire community.</p><p> </p><h2><span class="text--big"><strong>Drainage Systems Components</strong></span></h2><p>Understanding the basic components of drainage systems is crucial for selecting and maintaining an effective solution. Slope shape (uniform, convex, or concave), slope length, slope gradient, outlet position, type and size are key factors when designing a drainage system. Key components include:</p><p> </p><h3><span class="text--medium"><strong>1. Channel Drain Body Base</strong></span></h3><p>The channel drain body is the initial collection point for surface water. These drainage components come in various profiles:</p>
<ul><li><strong>V-shaped Channels</strong>: These channels have a V-shaped profile. This shape facilitates efficient water collection, provides faster flow, and requires less maintenance. V-shaped channels feature in <a href="/en-us/trench-drainage/bg-filcoten">BG-FILCOTEN systems</a>.</li></ul>

<ul><li><strong>U-shaped Channels</strong>: U-shaped channels provide a great capacity. They have a lower self-cleaning effect than the V-shaped channels due to their flat bottom and lesser hydrodynamics.</li></ul>

<ul><li><strong>Specialty shapes:</strong> Specialty channel shapes meet specific project needs. Examples include circular, elliptical, hexagonal (as seen in <a href="/en-us/trench-drainage/bg-gatic">BG-GATIC slot drains</a>), and rectangular channels (available in <a href="/en-us/trench-drainage/bg-flex">BG-FLEX channel drains</a> and cast-in-place systems). </li></ul>

<p>Alongside profiles, channel bases also come in different types. Users should choose the correct type for their installation requirements.</p>
<ul><li><strong>Type I</strong> channels like those in the <a href="/en-us/trench-drainage/bg-filcoten/one">BG-FILCOTEN one</a> and <a href="/en-us/trench-drainage/bg-filcoten/one-urban">BG-FILCOTEN one urban</a> range are self-supporting, meaning they do not require a concrete encapsulation.</li></ul>

<ul><li><strong>Type M</strong> channels are lighter but need a concrete encasement for stability like <a href="/en-us/trench-drainage/bg-filcoten">BG-FILCOTEN trench drains </a></li></ul>

<ul><li><strong>Cast-in-place channels</strong> are generally custom-built on-site using formwork. The installation of a cast-in-place trench drain is more challenging because it demands precise manual work and expert skills and specialized expertise. Furthermore, since their grates often are not fastened to any rail, they can generate noise when traversed by vehicles.</li></ul>
<h3><span class="text--big"><strong>2. Drainage Channels Grates</strong></span></h3><p>Drainage Channel grates allow water to flow into channel drain systems. They also limit debris collection and provide structural support. Such drainage grates come in different materials:</p>
<ul><li><strong>Durable metallic Grates:</strong> These grates use long-lasting materials like ductile iron, galvanized steel, stainless or corten steel. These materials offer varied load-bearing capacity or chemical resistance</li></ul>

<ul><li><strong>Composite Grates:</strong> Generally made from composite polymers, they often serve for aesthetic purposes. They also offer some chemical resistance properties.</li></ul>

<p>Drainage grates also come in different designs. Grate designs vary depending on their intended use. Consider the following factors when choosing drainage grates:</p><ul><li><strong>Water flow:</strong> Mesh grates, slot grates, longitudinal slot grates, and perforated grates are designed to optimize water flow. Different opening dimensions determine the flow rate. Half-inch slot openings yield a flow rate of 11 gallons per minute for each foot of slot. One-inch slot openings facilitate 18 gallons per minute for a foot of slot. 1¼” slot openings yield 27 gallons per minute for each foot of slot.</li><li><strong>Load levels:</strong> The structural design of the grate determines how much load it can carry. Load classes range from <strong>A15</strong> (light pedestrian traffic) to <strong>F900</strong> (heavy infrastructural loads), ensuring that the grates can support the specific load requirements.</li><li><strong>Health and safety:</strong> Drainage grates must comply with regulations such as the <a href="https://www.ada.gov/law-and-regs/design-standards/2010-stds/">American Disability Act</a> (ADA), which requires mesh openings of less than 13 mm for wheelchair access. Heel proof or heel safe designs with openings less than 8 mm wide are essential in urban areas.</li></ul><p>BG GRASPOINTNER provides an extensive selection of <a href="https://data.bg-graspointner.com/uploads/8052/BG-BLACKLABEL_deco-line-EN.pdf">premium decorative grates for trench drains</a>, designed to meet the highest aesthetic standards while delivering exceptional functionality.</p><p> </p><h3><span class="text--big"><strong>3. Catch Basin of the Drainage Channel</strong></span></h3><p>The catch basin, or sump unit, is a submerged part of the trench drain system component that attaches to an outflow pipe and facilitates the effective disposal of accumulated water. The sump features a sediment bucket that collects and removes debris like silt, cigarette butts, and leaves. Debris removal ensures drains require less upkeep and prevents clogging.</p>

<h2><span class="text--big"><strong>Drainage Channels Material</strong></span></h2><p>The drainage system material affects performance, durability, and suitability for different applications. Here are the most common drainage system materials to consider:</p><p> </p><h3><span class="text--big"><strong>Drainage Channels Made of HPC Concrete (High-Performance Concrete)</strong></span></h3><p><strong>BG-FILCOTEN</strong> products represent a significant advancement in trench drain systems, thanks to High-Performance Concrete (HPC). Traditionally, HPC was limited to large-scale structural applications due to its exceptional strength and endurance. Since the invention of lighter, thinner, and more durable drainage channels, BG-Graspointner has completely changed how we use HPC channels.</p><p> </p><p>BG-FILCOTEN components are roughly up to 70% lighter than traditional concrete prefabricated products, making them easier to handle and install. Despite its reduced weight, a BG-FILCOTEN concrete drainage channel can bear heavy loads. These channel drains can also withstand significant temperature changes, enhancing longevity.</p>
<h3><span class="text--big"><strong>Stainless Steel Drainage Channels</strong></span></h3><p><a href="/en-us/trench-drainage/bg-flex">BG-FLEX drainage channels</a> show the benefits of using stainless steel for trench drain systems. Stainless steel is a premium material often chosen for its hygienic properties. Due to its non-porous nature, the stainless drainage channel resists bacterial growth and is easy to clean.</p><p> </p><p>These features make stainless steel drainage systems ideal when hygiene is vital. Applications include food processing, building envelope, epoxy-floor parking lots balconies and terraces.</p>

<p><strong>BG-FLEX drains</strong> also have a timeless aesthetic appeal. A stainless steel drainage channel will look sleek and modern, combining well with various architectural styles. Steel is popular for visible areas around building envelopes where appearance matters.</p><p> </p><h3><span class="text--big"><strong>Galvanized Steel Channel Drains</strong></span></h3><p><a href="/en-us/trench-drainage/bg-gatic">BG-GATIC slot drains</a> use galvanized steel - a popular material for heavy-duty applications. The hexagonal slot drain product concept makes it heavy duty compliant and suitable for infrastructure projects like airports, harbors, and parking lots.</p><p> </p><p>Galvanized steel's durability and pressure resistance make it ideal for creating slot drains with hexagonal bodies. These drains are particularly effective in managing large volumes of water under intense load conditions.</p>

<h3><span class="text--big"><strong>Drainage Channels Made of </strong>Polymer (Plastic)</span></h3><p>Plastic drainage channels feature polypropylene, HDPE, PVC, Laminated Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic (GRP), or Sheet Material Compound (SMC). Plastics are valuable due to their reduced weight and chemical resistance. However, plastics are brittle, do not bond well with concrete foundations, and are prone to deformation under high temperatures. Plastic trench drains are subject to high expansion and contraction due to temperature changes. Plastic trench drains may contain toxic compounds like VOCs, styrene, or cobalt. Despite these drawbacks, plastic channels remain popular due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. That said, BG Graspointner does not focus on plastic drainage systems. Instead it offers a range of environmentally-friendly channel systems.</p><p> </p><h2><span class="text--big"><strong>How to Choose the Right Drainage System</strong></span></h2><p>Choosing the appropriate drainage system for your site can be overwhelming. Performance and durability rely on <strong>selecting suitable materials</strong> and <strong>ensuring proper installation</strong>. Use the selection process below to guide the process:</p><ul><li><strong>Determine the surface area that needs drainage:</strong> This will impact the size and length of the drainage system required.</li><li><strong>Evaluate how the drainage system will be used:</strong> Will it drain a parking lot, walkway, or industrial site? Different uses place varying demands on the system. For instance, the <a href="/en-us/bg-blog/load-classes-north-america">load class</a> determines the system’s ability to withstand various types of traffic.</li><li><strong>Calculate peak water flow rates based on local rain intensity:</strong> This metric is vital to prevent flooding and is typically measured in millimeters or gallons per hour.</li><li><strong>Consider local environmental regulations:</strong> <a href="/en-us/trench-drainage/bg-filcoten/green">The drainage system must meet environmental regulations</a> such as treating rainwater before disposal. You may need to add filtration or sedimentation systems.</li><li><strong>Assess the slope of the ground:</strong> Gradients and contours impact water flow and drainage efficiency.</li><li><strong>Determine how many outlets are needed</strong> to drain water and prevent clogs.</li><li><strong>Think about aesthetics:</strong> Does your project have any visual preferences for the site or user community?<br> </li></ul><h2><span class="text--big"><strong>Conclusion</strong></span></h2><p>There's a lot to consider when choosing the right trench drainage system, and contractors should always consult experts to meet their goals.</p><ul><li>Drainage systems components include grates, catch basins, and installation supports.</li><li>Trench Drains can be self-supporting or concrete encased. Choosing modern self-supporting trench drains can significantly reduce installation costs.</li><li>Trench Drains come in different profiles, from V-shapes and U-shapes, to hexagonal designs. Each design has unique properties and applications.</li><li>Trench Drains materials range from HPC concrete to galvanized steel and plastic. Materials have specific strengths and limitations. Choices should align with project demands, from rainfall intensity to traffic load.</li></ul><p>Expert assistance from BG-Graspointner considers all these elements, resulting in effective, durable drainage solutions. For further assistance, contact our experts today.</p>
